At Asian Eye Hospital we provide treatment for an extensive range of pediatric eye problems such as sight-threatening conditions like pediatric glaucoma, cataract and congenital opacities of the cornea.
We also have comprehensive services in:Pediatric ophthalmology is a sub-speciality of ophthalmology concerned with eye diseases, visual development, and vision care in children. Pediatric ophthalmologists are specially trained to manage the following disorders:
Squint or strabismus is a misalignment of the eyes so that the eyes do not point in the same direction. Squint can itself lead to amblyopia or lazy eye. More importantly squint if present since childhood can itself lead to loss of three dimensional vision or depth perception (stereopsis). Many cases can be treated with glasses. Orthoptic exercises are useful in some cases. Prism trials can be used as a temporary or permanent measure. Squint can itself lead to cosmetic disfigurement, in addition in children there is a risk of amblyopia.
Under such circumstances, it is important that one corrects the squint early. In addition there is a beneficial effect of correction of squint even in older adults as there is improvement in binocular vision. The simplicity and ease of surgery means some patients start work the next day after surgery. The results are very good with a proper clinical assessment and surgery.
Convergent squint can be corrected many a times by glasses. Early correction is recommended especially in the convergent squints as there is a higher risk of amblyopia and loss of binocularity.
Divergent squint can again be corrected with glasses, but more commonly needs surgery.
Vertical squints are tackled especially in cases of superior oblique muscle palsy or Brown Syndrome and need proper planning, surgery is however easy to perform.
Nystagmus can also be considered as a form of squint and indications for surgery include head posture or need for dampening the nystagmus. Newer surgeries for this condition give successful outcomes.

A diagnosed squint needs prompt treatment, otherwise there is a serious risk of complications, such as amblyopia (lazy eye). The younger the patient is, the more effective treatment is likely to be.
Glasses - if the child is found to hypermetropia (long-sightedness), they will be prescribed glasses which usually solve the squint.

Eye patch - this is worn over the good eye to get other eye, the one with the squint, to work better.
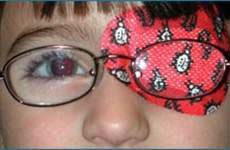
Orthoptic Exercises -The doctor may also prescribe eye drops, and get the patient to do specific eye exercises.
Botulinum toxin injection (Botulinum) - this is injected into a muscle on the surface the eye. The doctor may recommend this treatment if no underlying cause can be identified, and if signs and symptoms come on suddenly. The injected muscle is weakened temporarily, which often helps the eyes to align properly.
Surgey - surgery is only used when other treatments have not been effective.can restore binocular vision, as well as realign the eyes. The surgeon moves the muscle that connects to the eye to a new position - sometimes both eyes need to be operated on to get the right balance.
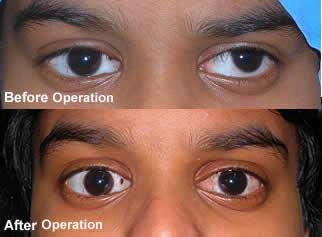
The simplicity and ease of surgery means some patients start work the next day after surgery.The results are very good with proper clinical assessment and surgery.